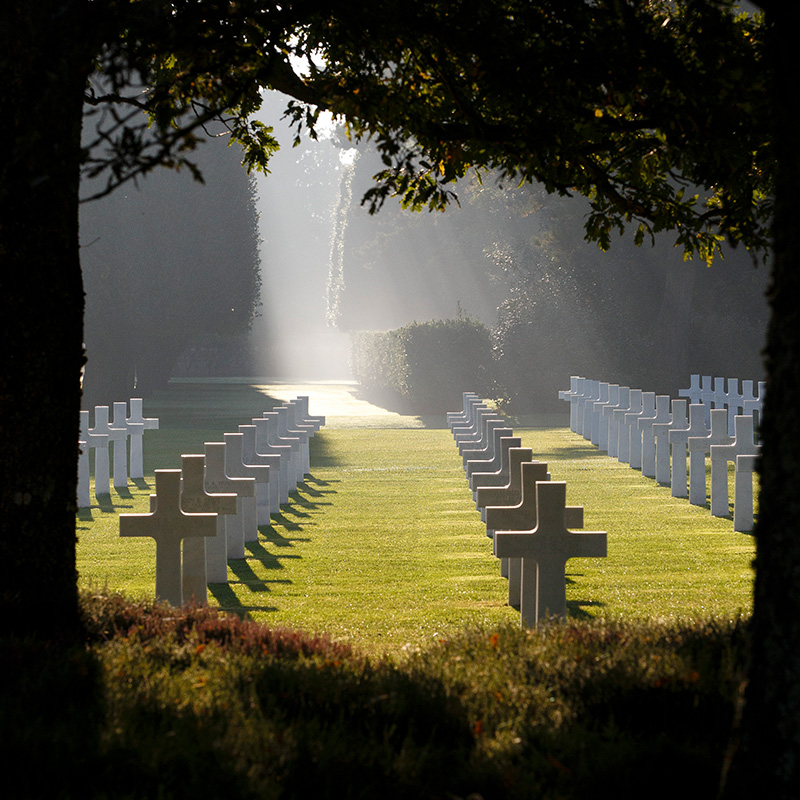
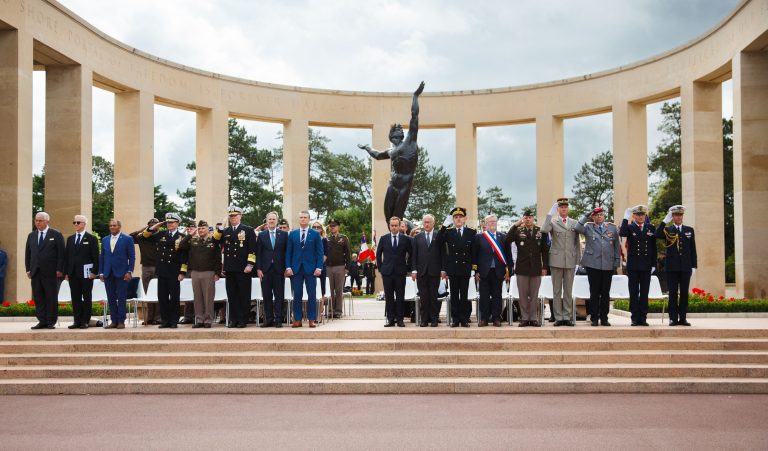
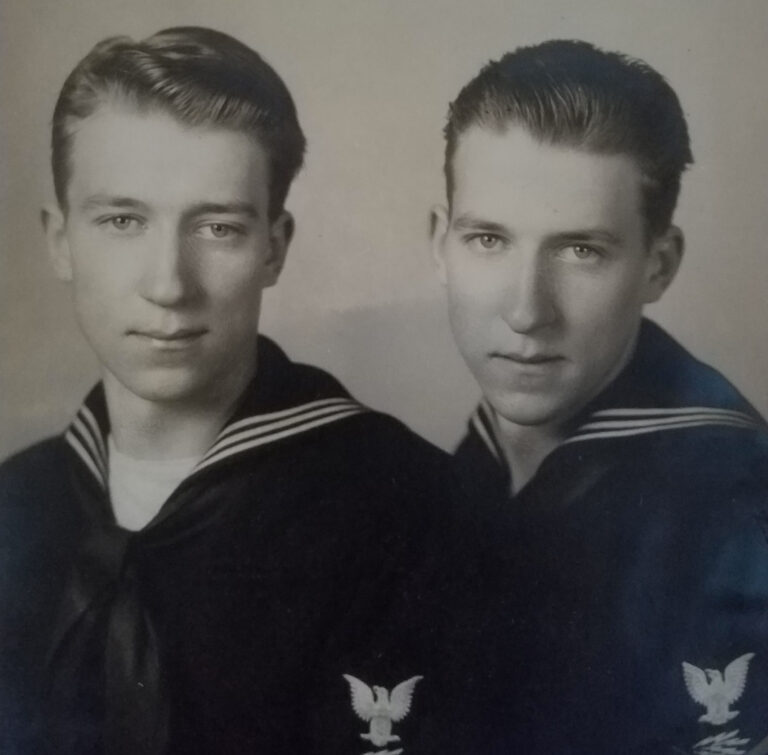
The Normandy American Cemetery and Memorial in France is located in Colleville-sur-Mer, on the site of the temporary American St. Laurent Cemetery, established by the U.S. First Army on June 8, 1944 as the first American cemetery on European soil in World War II. The cemetery site, at the north end of its half mile access road, covers 172.5 acres and contains the graves of 9,389 of our military dead, most of whom lost their lives in the D-Day landings and ensuing operations. On the Walls of the Missing, in a semicircular garden on the east side of the memorial, are inscribed 1,557 names. Rosettes mark the names of those since recovered and identified.
The memorial consists of a semicircular colonnade with a loggia at each end containing large maps and narratives of the military operations; at the center is the bronze statue, “Spirit of American Youth Rising from the Waves.” An orientation table overlooking the beach depicts the landings in Normandy. Facing west at the memorial, one sees in the foreground the reflecting pool; beyond is the burial area with a circular chapel and, at the far end, granite statues representing the United States and France.
In 2007, the Normandy Visitor Center opened. The $30 million visitor center was dedicated by the American Battle Monuments Commission (ABMC) on June 6, 2007 during the commemoration of the 63rd Anniversary of D-Day. The center is sited in a wooded area of the cemetery approximately 100 meters east of the Garden of the Missing.
Learn more about the architecture, exhibits, inscriptions, and the project team.
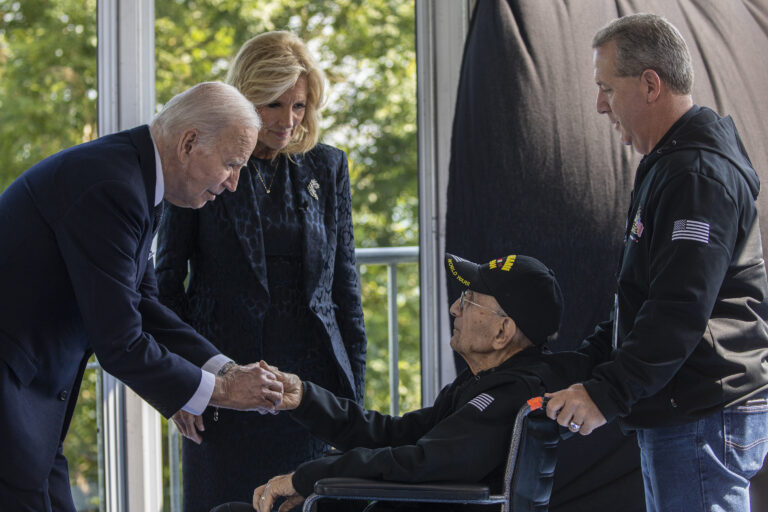
Normandy is ABMC’s most visited cemetery, receiving more than one million visitors each year. To plan a site visit, a visit to a relative’s grave, request a group visit, special tour, or wreath laying ceremony, please contact NormandyVisits@abmc.gov.
Due to security concerns, the pathway from Normandy American Cemetery to the beach was closed to the public in 2016. However, public beach access is available nearby.
The flag lowering ceremony is held one hour before the cemetery closes to the public.
For questions, please contact us at NormandyVisits@abmc.gov.
Normandy American Cemetery sits on a cliff overlooking Omaha Beach and the English Channel, east of St. Laurent-sur-Mer and northwest of Bayeux in Colleville-sur-Mer.
Due to security concerns, the pathway from Normandy American Cemetery to the beach was closed to the public in 2016. However, public beach access is available nearby.
The massive Allied assault on the Normandy coastline on June 6, 1944 aimed to liberate France and drive into Nazi Germany.
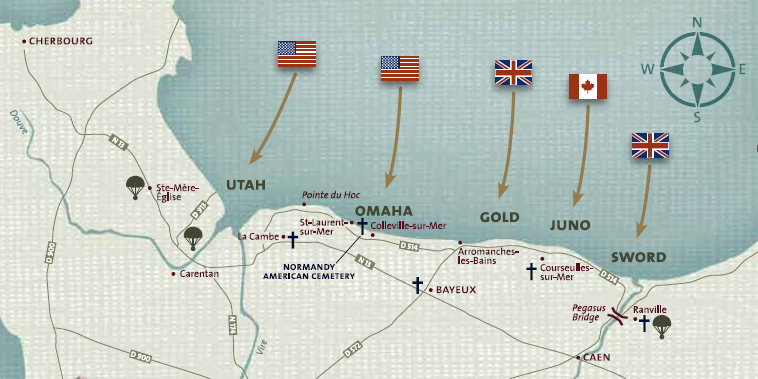
Before dawn on June 6, three airborne divisions—the U.S. 82nd and 101st and the British 6th—landed by parachute and glider behind targeted beaches. Allied naval forces, including the U.S. Coast Guard, conveyed assault forces across the English Channel. Beginning at 0630 hours, six U.S., British and Canadian divisions landed on Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno and Sword Beaches in history’s greatest amphibious assault.
The U.S. 4th Infantry Division pushed inland from Utah Beach. To the east, on Omaha Beach, the U.S. 1st and 29th Infantry Divisions battled German resistance over a beach bristling with obstacles. To reach the plateau where Normandy American Cemetery stands, troops fought across an open area of up to 200 yards, and attacked up steep bluffs. By day’s end, the Americans held fragile control of Omaha Beach.
On Gold, Juno and Sword, British and Canadian divisions forged ahead. In less than a week, the Allies linked the beachheads and pressed onward.
Over the next three months, the Allies battled German troops throughout Normandy. British and Canadians freed Caen. Americans liberated Cherbourg and staged a dramatic breakout near St. Lô. Allied troops, joined by French and Polish units, encircled and annihilated German troops at the Falaise Pocket while surviving units fled eastward. The way was now open to advance toward Paris and then to Germany.
 An official website of the United States government. Here's how you know.
An official website of the United States government. Here's how you know. 



















